Fantastic new ideas, market research, user feedback - you have everything to create the perfect products. But how do you decide which tasks or ideas to tackle first?
Whatever choice you make, you must justify it to your shareholders and your team. And what better way to do that than with a prioritization score?
In this highly competitive world, where every task and idea competes for attention and resources, mastering the art of prioritization is crucial. Using a framework such as RICE prioritization (Reach, Impact, Confidence and Effort) can help you quantify your ideas and provide a basis for selecting a specific idea over others.
This article will discuss the details of the RICE scoring model and how it can transform your decision-making.
What is RICE prioritization?
The RICE model is a prioritization framework used in product management and project development to evaluate and prioritize tasks, resources or projects, scoring them based on four criteria.
RICE means:
- R - Reach: Reach measures the number of users or stakeholders who will be affected by a given task or resource.
- I - Impact: Impact assesses the potential positive effect that a task or resource can have on the product, users or business goals.
- C - Confidence: Confidence represents the level of certainty or trust that the team has in its estimates of impact and effort for a given task or resource.
- E - Effort: Effort measures the resources, including time, manpower and budget, needed to complete a task or implement a feature.
The RICE method helps to provide structure and objectivity during decision-making, facilitating better management of priorities and objective decisions.
The formula for the RICE method is as follows:
RICE Score = (Reach x Impact x Confidence) / Effort
This score makes it easier to decide on the order of the project and the priority tasks.
The origin of the RICE scoring model
Sean McBride, a former product manager at Intercom, co-developed the RICE framework. He and his colleagues struggled to find a prioritization framework that best met their decision-making needs.
One of the common problems product managers face is selecting projects based on personal perspectives or with a broader scope. So McBride developed the RICE score to solve problems related to objective decision-making.
How does RICE prioritization work?
Previously, we briefly discussed the components of the RICE score. In this section, we'll delve into them one by one.
Reach
The first component of the RICE framework is Reach. It measures the number of people a project affects in a given period. The greater the reach, the greater the number of people the project will benefit. It is usually measured over a month or quarter.
To calculate reach, you can define which category of users you are considering. However, it's best to use actual measurements from product metrics.
For example, suppose you are launching a new collaboration feature on your evaluation platform, with 100,000 monthly active users.
The first step is to identify the potential audience or user base that this feature will impact over the course of a month (or quarter). Let's say you estimate that this feature is relevant to 40% of your user base. Therefore, your reach is 40,000 users.
Impact
Impact assesses the potential effect of a task, resource or project on individual users. In reach, you measure the number of people impacted by a resource. In impact, you measure how much people are affected.
So, in the example above, you can see how much the collaboration feature will increase user engagement and team collaboration.
We usually measure impact with a higher goal. McBride used a multiple choice scale for this:
- 3 = Massive impact
- 2 = High impact
- 1 = Average impact
- 0.5 = Low impact
- 0.25 = Minimum impact
You don't have to use the same scale. You can choose the one that suits your needs.
A crucial point to remember when measuring this is that you need to set clear goals for each project before using the RICE score. And the best way to do this is by collaborating with your team and stakeholders. You can use a shared whiteboard to discuss ideas and communicate in real time.

Confidence
Confidence measures your certainty about your estimates of scope, impact and effort. This criterion is determined based on the answer to the following question:
What is your level of confidence in this resource and the scores given?
The answer is expressed as a simple percentage. McBride used the following multiple choice scale:
- 100% = High confidence
- 80% = average confidence
- 50% = Low confidence
Anything below 50% is a guess. Again, you can use whatever scale works best for you. From 10% intervals to 25% intervals, use what best suits your needs. However, the key here is to be totally honest.
User context, research and experimentation should support a high trust score. You can also use product backlog management tools for advanced analysis and insights.
The confidence score allows you to ensure that your decisions are really based on data. If you have high reach and impact scores, but a low trust score, you can explore how to improve.
Effort
Effort tells you the total amount of work you need to do to complete the project. You should consider the time of your team members, including product, design and engineering teams. It is estimated in person-months, the amount of work a team member can do in a month.
Unlike other factors, effort is a negative factor. Therefore, the greater the effort, the less viable your project will be. More effort means you need more time to finish the project.
For example, designing, testing, debugging and launching the feature in our example could take three months. Assuming you have a team of 5 people, your effort score would be 15 person-months.
Talking to your team members is best to get an accurate picture.
How to optimize the RICE prioritization process
The use of product management models and software can optimize your RICE prioritization process.
ClickUp is a project management tool that simplifies product management and makes it faster and easier. You can use ClickUp for Product Management to map out your product vision, simplify prioritization and build roadmaps that connect teamwork.
Also, read up on work prioritization tools to help you better prioritize your daily work.
Here's how:
ClickUp task visualization

Task views offer a unique way of visualizing your tasks. You can select from views including list, activity, board, table and team. You can list tasks, write updates, ask contextual questions about different tasks and generate task summaries.
Ask members about their specific tasks to estimate your team's effort (face-to-face hours/weeks/months).
Custom fields
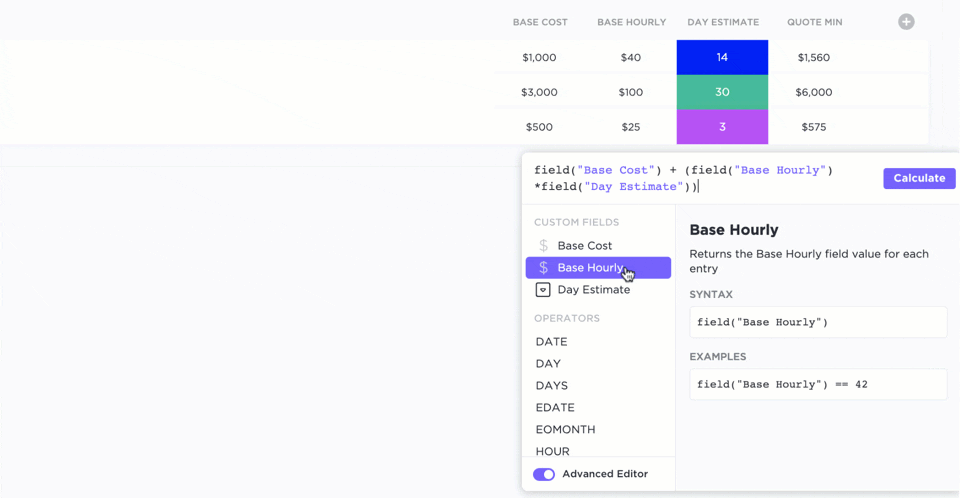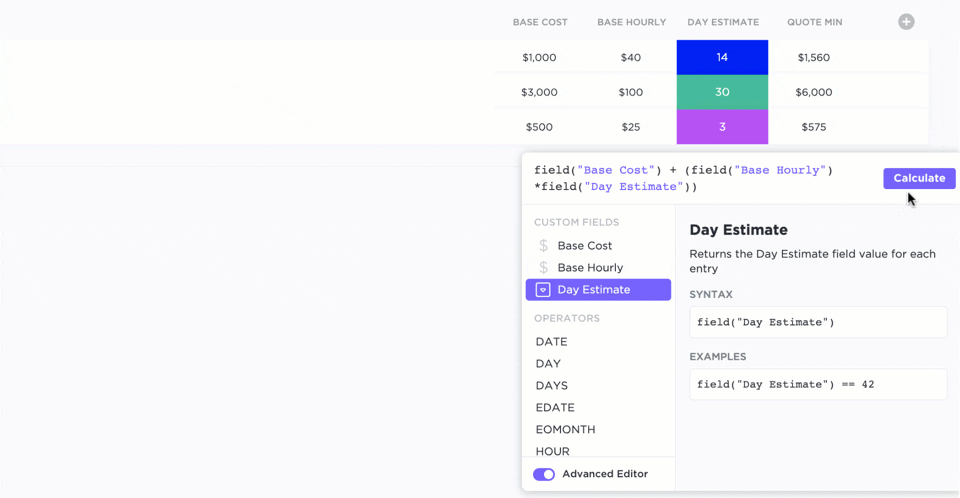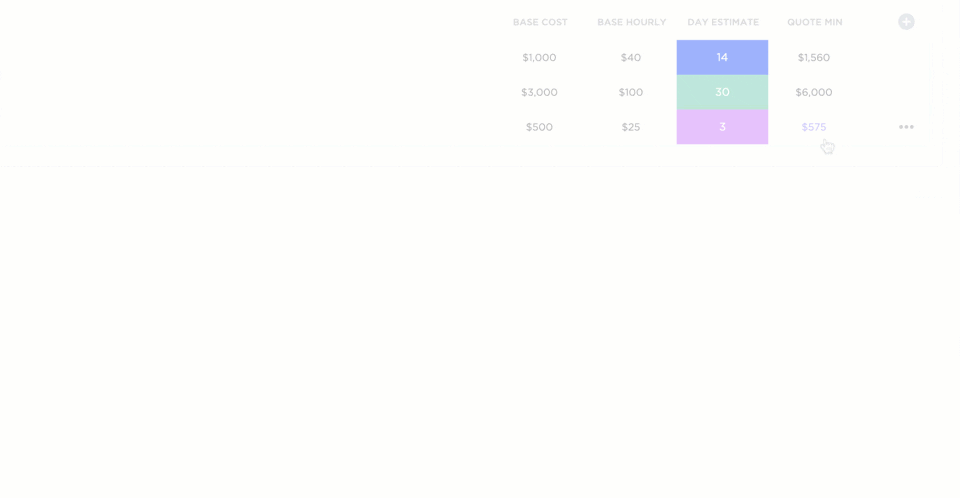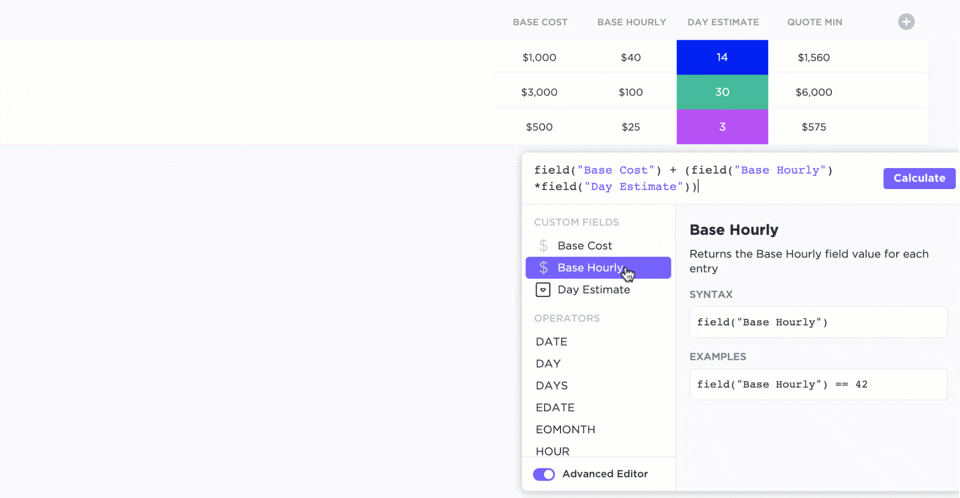
With custom fields, you can personalize your workspace and add different types of data. You can use advanced formulas, mathematical functions, date and time functions, etc. This is perfect for adding scores to your RICE components.
ClickUp also allows you to create fields, edit them and show and hide them when necessary.
ClickUp Gantt Charts
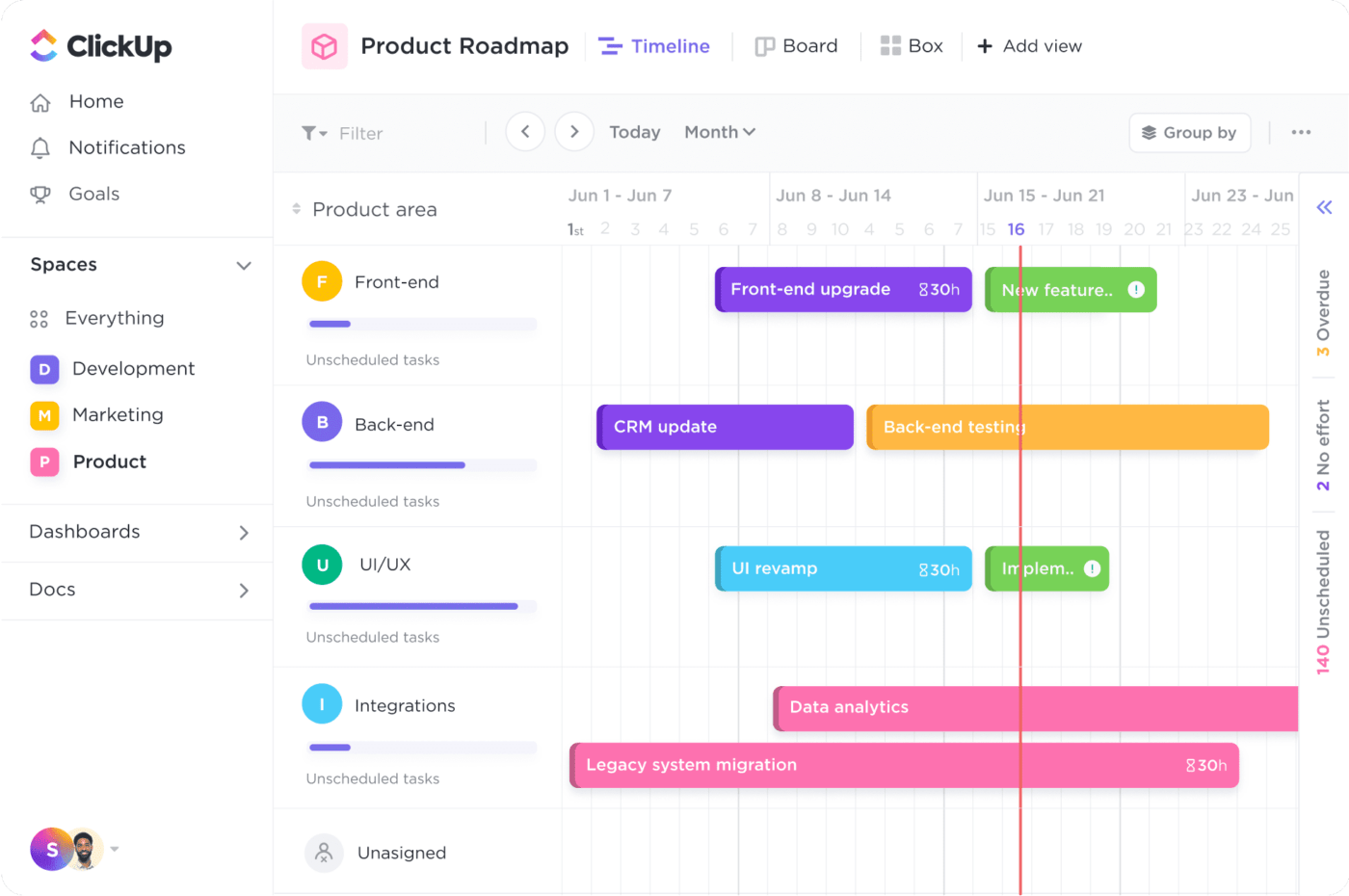
You can use ClickUp Product Planning to build roadmaps, set milestones, add templates, visualize better and much more. Gantt charts allow you to plan for success and visualize project schedules. You can easily compare and collaborate, manage priorities and track progress.
Click targets
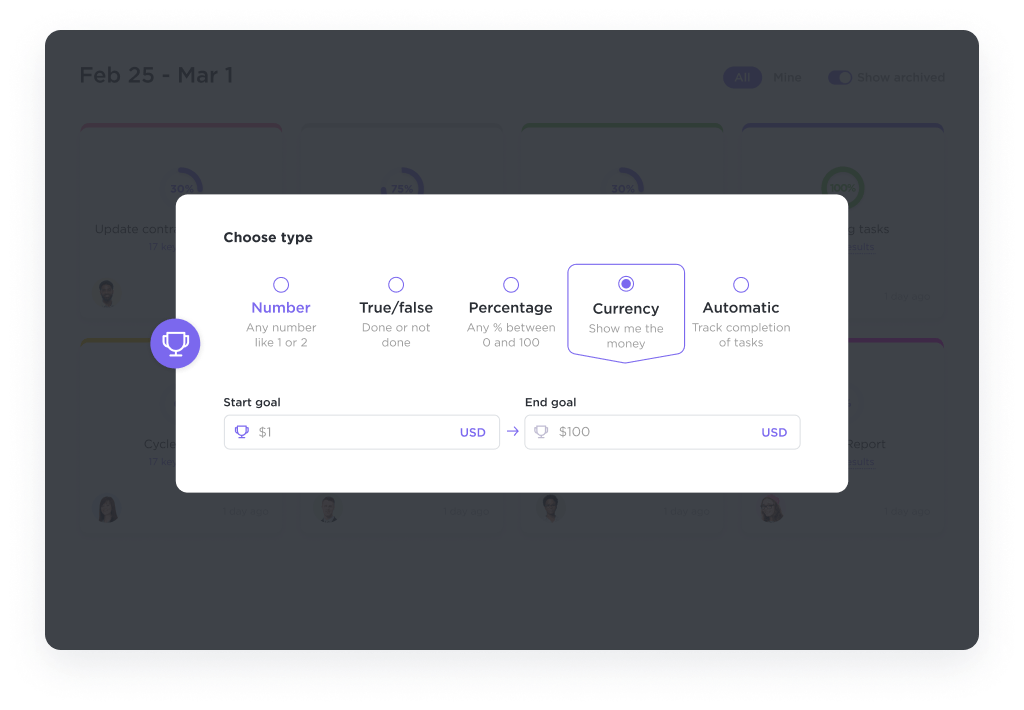
The RICE prioritization framework works best when your team and stakeholders agree on the goals you want to achieve using different ideas. ClickUp Goals helps you align team objectives, set clear goals, measure success and manage all your goals in one place.
Prioritization models
The use of prioritization and product planning models increases efficiency, improves decision-making and ensures the effective allocation of resources. Some models you can use are:
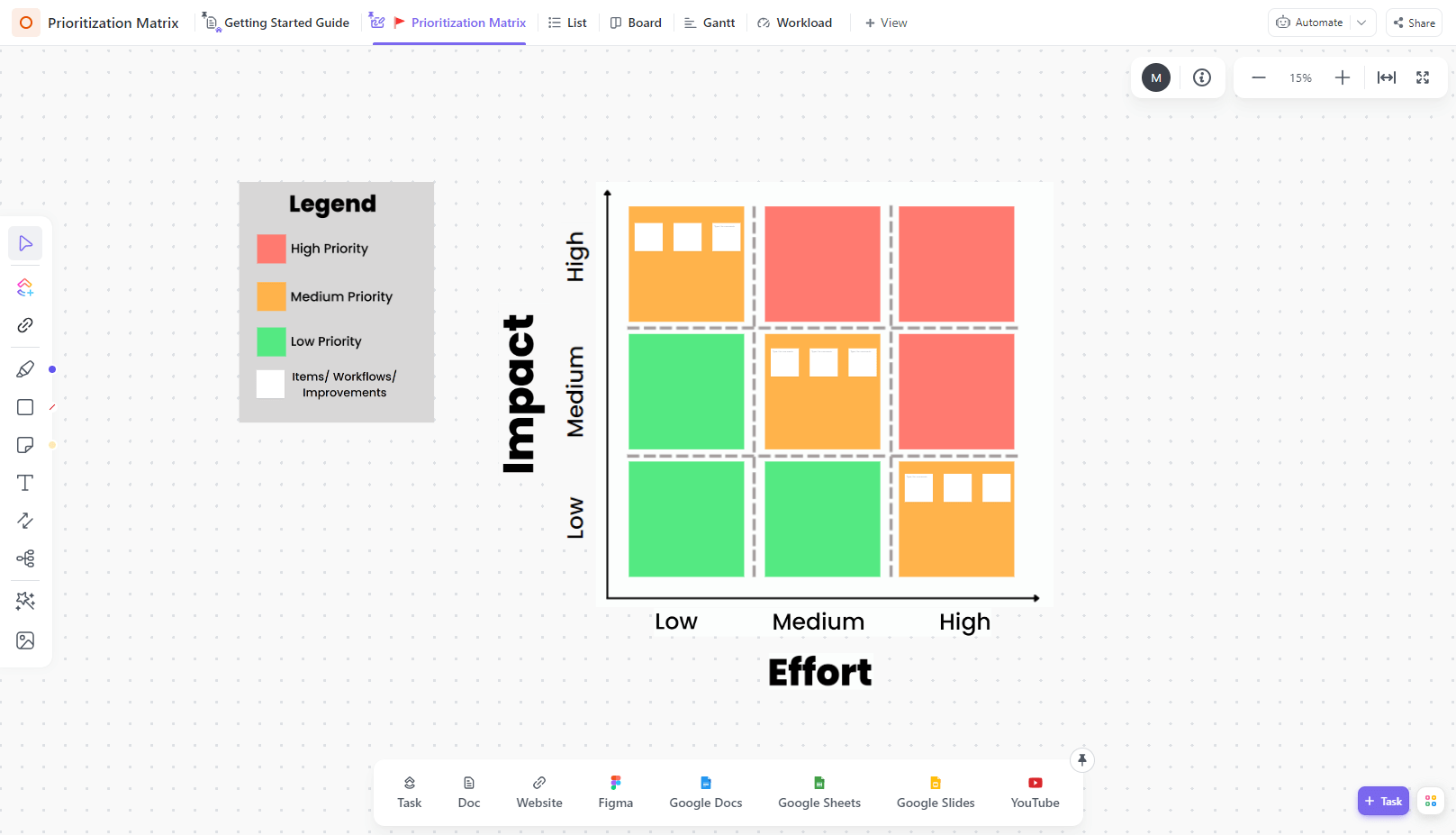
- Evaluate tasks based on their impact and effort levels using the ClickUp prioritization matrix model
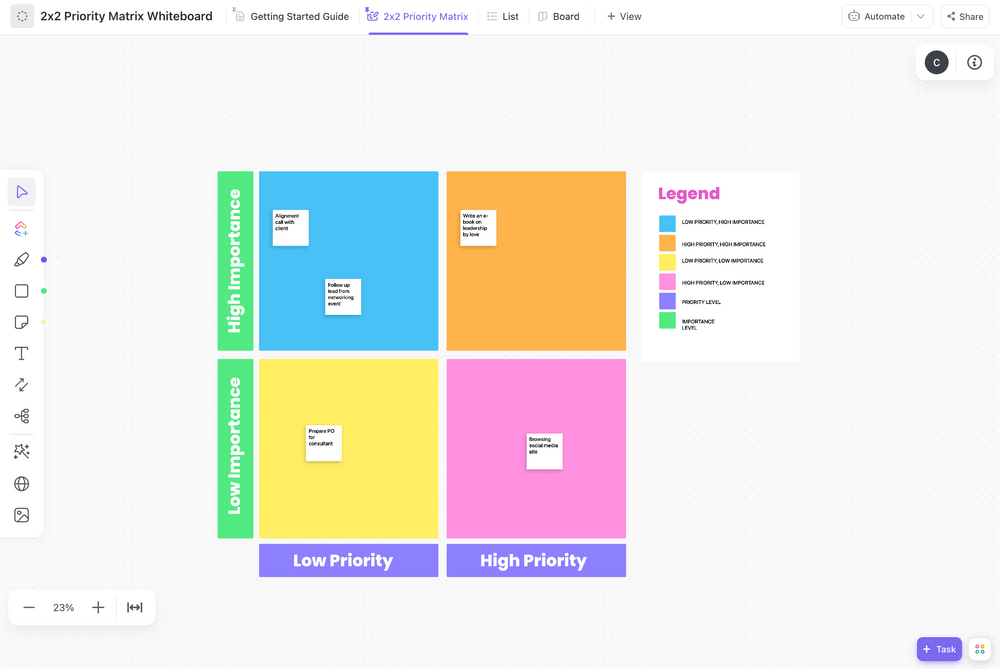
- Manage ideas and proposals using the colorful prioritization whiteboard template
- Describe your development process and follow timelines using the new product development model. This model also helps to align teams in relation to milestones
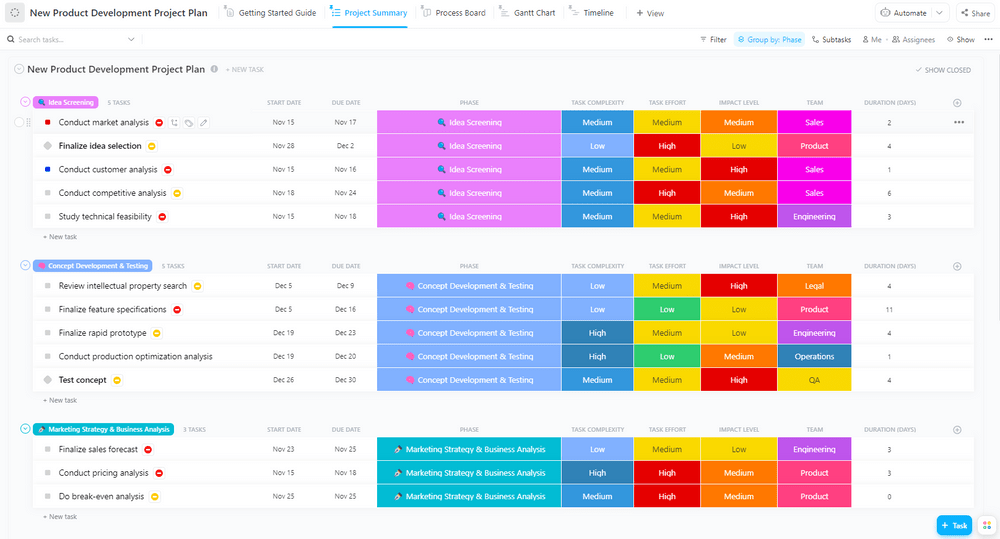
- Visualize your product development process and get detailed insights into each component using the product roadmap template

Pros and cons of using the RICE prioritization method
Like other frameworks, the RICE prioritization method has advantages and shortcomings. Although it quantifies your ideas, it can also be inaccurate. Let's understand these pros and cons in detail.
Pros
Here are some of the pros of prioritizing RICE:
1. better communication
It enables better communication using a standardized scoring system and helps communicate priorities in a straightforward manner. It helps everyone identify high-priority tasks and better manage their priorities. In addition, the use of product management tools also improves collaboration and the sharing of updates in real time.
2. Clear prioritization
The RICE score offers a clear, numerical prioritization of tasks or resources. Thus, you can sort the list by priority, focusing more on high-priority items. This allows you to use your resources, including time and money, efficiently.
3. Easy to understand
RICE uses a simple scoring system based on four factors, so people can use it without product management certification or qualification. Team members, stakeholders and decision-makers can easily use it to understand the reasoning behind various prioritization-related decisions.
4. Considers significant factors
The score prioritizes four main factors: reach, impact, confidence and effort. These are among the most crucial factors in assessing the viability of an idea and whether an idea is viable.
5. Prioritization based on data
The RICE framework offers a quantitative approach to prioritization, eliminating personal prejudices and subjective opinions. It is based on measurable, data-driven facts that help you make informed decisions.
6. Categorical flexibility
It offers flexibility by allowing teams to adapt and apply it to different categories of tasks, products and resources. Whether it's new product features, bug fixes or process improvements, RICE can be adapted to suit different contexts.
7. Helps with alignment
The RICE score helps align team members and stakeholders and ensures that everyone is working towards the same goals. It also promotes a collaborative and more focused working environment.
Cons
Some of its cons include:
1. Can be inaccurate
One of the main disadvantages of RICE is that it involves a lot of estimates and assumptions. We can overestimate the values, which will make the score inaccurate. In addition, the confidence factor is subjective based on the person's understanding and confidence in the task.
It is therefore crucial to be as precise as possible. The necessary metrics can help you do this.
2. Less customer-centric
Another problem with this method is that it is not customer-centric. Factors such as reach and impact capture some aspects of customers. However, crucial elements such as preferences, feedback and emotional aspects are not considered.
Even with reach and impact, these figures are defined by what the product manager believes would be the reach and influence of a given product over a given time.
3. Easily manipulated
The assignment of scores in RICE is not entirely free of subjective judgment. Different product managers have different prejudices which can lead to inconsistent scores. Some may intentionally raise or lower scores, especially in the reliability component. One way to avoid this is to involve several people in the scoring process.
Variations and alternatives to RICE
Here are some of the alternatives to the RICE prioritization model:
BRICE
BRICE Scoring is an excellent alternative to the RICE framework for prioritizing product management. It is similar to RICE, except that it measures an additional factor called Business Importance.
Therefore, the five factors measured are Business Importance, Reach, Impact, Confidence and Effort. Business Importance measures how the product you are considering aligns with the strategic objectives of the business. It is usually scored between 1 and 3, with 3 being the highest score (representing that the product is fundamental to the business).
To calculate the BRICE score, you can use this formula:
BRICE Score = (Business Importance x Reach x Impact x Confidence) / Effort
Value vs. Effort
Value vs. Effort is a prioritization method that focuses on value and effort and allows you to evaluate different resources. The idea is quite simple: you measure the benefit the idea will bring you and compare it to the effort required to achieve it.
Assign each resource a value score and an effort score to calculate it. High value and low effort features are clear winners. High value, high effort and low value, low effort come next. It's best to avoid low-value, high-effort resources.
Although the method gives a clear idea of prioritization, one of its disadvantages is that it is difficult to estimate value and effort.
SWEET RICE
The SU-RICE framework has two imperative factors not included in the RICE model: source and User Persona. This is a more comprehensive framework, as it also considers from which source you are getting ideas for product features and user persona, as well as reach, impact, trust and effort.
You can consider four sources: potential customer, customer, market or competition and internal, and list them according to priority. This structure provides a more detailed understanding of the context and potential impact of a task or resource.
Story mapping
Story mapping prioritizes features based on how your customers plan to use the product. It's not a scoring model. Instead, it involves collecting user stories that describe a feature and mapping them.
This provides an outline of the product and lists sub-tasks and details of each task. This method is highly customer-centric and allows you to have an overview. By ideating, you also create a visual document that reminds everyone of your goals.
Prioritize better using the RICE Framework with ClickUp
The RICE framework is an excellent method for deciding which ideas deserve attention first. It quantifies ideas and makes it easier to prioritize them. It also takes little time to use and helps you make objective decisions.
A few things to remember when using the model:
- Focus on a goal
- Your scoring system affects your score
- Involve your team during the scoring process to make it more objective
- Use product management templates for better visualization
- Regularly review and update the score
- You may undervalue technical debt, so consider it separately in your prioritization system
A complete product management tool like ClickUp offers better alignment, collaboration, visualization and templates during prioritization.



LATEST VIDEOS
Find out which license is best for you and your team
Take the opportunity to check out other content on ClickUp
How office design affects productivity
We all know that running a business is difficult, managing a team is difficult, even [...]
Aug
Understanding the differences between Agile and Waterfall
Want to understand the differences between Waterfall and Agile project management? Although both are [...]
Jun
Advantages of Using ClickUp for Financial Planning
Financial planning is an essential process for any business or project, as it allows [...]
Nov
Agile software development lifecycle (Definitive Guide 2023)
Agile software development: Want to learn about SDLC Agile? It sounds like a complicated lesson [...]
Jun
What brand monitoring is and why it boosts your business growth
Brand Tracking: You probably know your conversion metrics by heart, CTRs from [...]
Sep
ClickUp Release 3.40: Limited roles for Members, guests in Chat and AI enhancements
In this week's ClickUp updates, we bring you new features in Chat, AI and more. Let's go [...]
Jan
ClickUp Release 3.24 : This Week's ClickUp Updates
Salesforce Integration, Slack Link Preview, Custom List Icons and More. A [...]
jul
ClickUp release 3.47: AI-suggested custom fields, Google Calendar automations and much more!
This week, we bring you AI-suggested custom fields, Google Calendar automations and [...]
sea